Search Results
Results for: 'Enzymatic breakdown of ATP'
By: HWC, Views: 6548
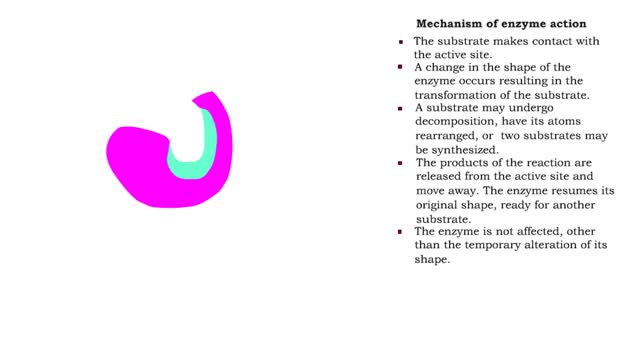
Ō¢Ā The substrate makes contact with the active site. Ō¢Ā A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. Ō¢Ā A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. Ō¢Ā The products of the reaction...
By: HWC, Views: 6815
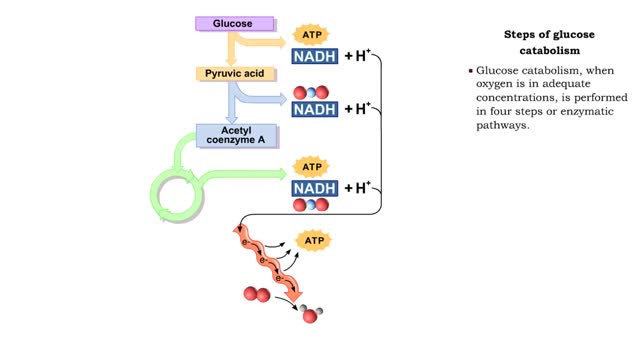
ŌĆó During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. ŌĆó The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. ŌĆó The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. ŌĆó Glucose cat...
Nucleic acid digestion -small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 6731
Nucleic acid digestion, which takes place in the small intestine, involves: ŌĆó Pancreatic nucleases. ŌĆó Brush-border enzymes in the small intestine. ŌĆó Nucleic acids enter the small intestine dissolved in gastric chyme. ŌĆó As gastric chyme enters the duodenum of the small intestine, p...
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 6617
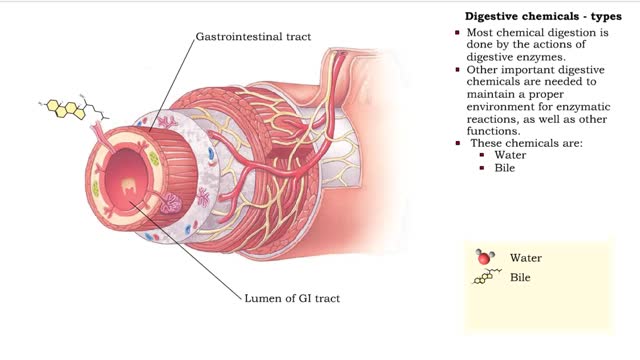
ŌĆó Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. ŌĆó Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. ŌĆó Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. ŌĆó O...
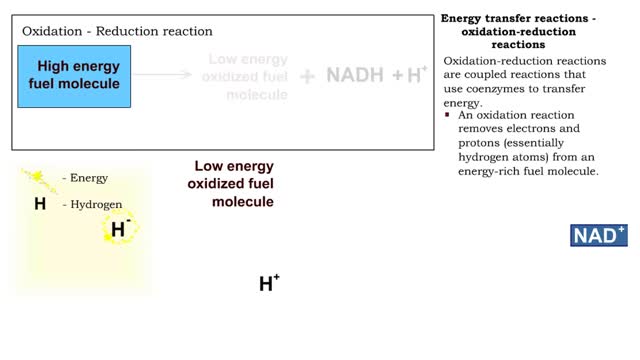
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 7195
Ō¢Ā Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. Ō¢Ā Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. Ō¢Ā Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
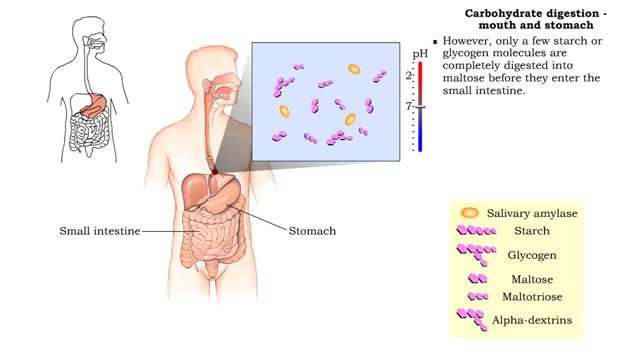
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 6412
ŌĆó Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: ŌĆó Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. ŌĆó Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. ŌĆó In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. ŌĆ...
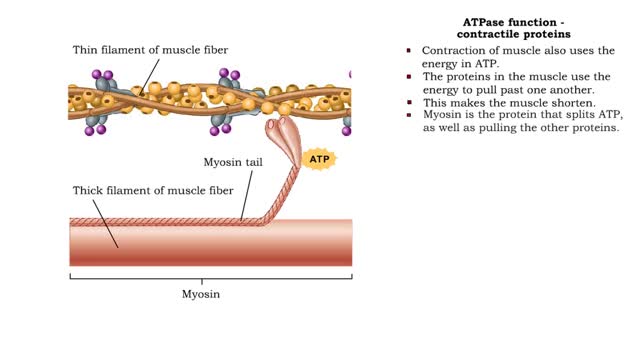
ATPase function - membrane transport, contractile proteins and synthesis
By: HWC, Views: 7039
ŌĆó Energy from ATP is used to move ions across the cell membrane during active transport. ŌĆó This membrane protein transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. As such, it is called a sodium-potassium pump. ŌĆó Because this pump also acts as an enzyme to hydrolyze ATP it i...
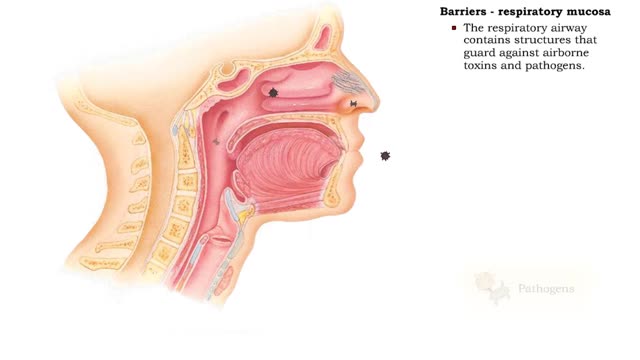
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 6879
ŌĆó Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. ŌĆó Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. ŌĆó Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. ŌĆ...
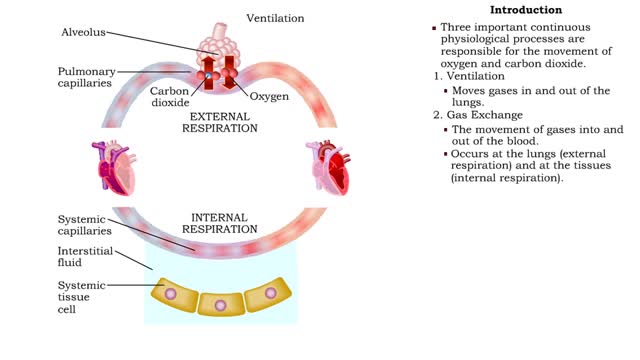
By: HWC, Views: 6751
ŌĆó The respiratory system is responsible for the movement of gases involved in cellular metabolism. ŌĆó Oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is generated during the aerobic breakdown of glucose and other fuel molecules in order to produce ATP. ŌĆó Three important continuous physiological pro...
Advertisement